一、 网络的相关概念
- 网络通信: 就是将数据通过网络从一台设备传输到另一台设备;
- 网络: 多台设备通过一定物理设备连接起来构成了网络;
1. ip
- 每台计算机在网络中的唯一身份标识;
- ipconfig 命令可以查看 ip 地址;
- IPv4:点分十进制 xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx , 如 192.168.199.198 - 每个十进制的范围 0 ~ 255;
2.域名、端口
- 域名: 解决 ip 难记的问题,通过 http 协议,映射到 ip 地址上
- 端口: 程序在单个设备中的唯一入口;
- 范围: 0 ~ 65535 , 其中 1~1024 已经被占用,不建议使用
3. 通讯协议
TCP/IP : 中文译名为传输控制协议/因特网互联协议,又叫网络通讯协议
这个协议由网络层的 IP 协议和传输层的 TCP 协议组成的。
TCP 协议:
- 使用 TCP 协议前,需要先简历 TCP 连接,形成传输数据通道;
- 传输前,采用“三次握手” 方式,是可靠的;
- TCP 协议进行通信的两个应用进程: 客户端、服务端;
- 在连接中可进行大量数据的传输;
- 传输完毕,需释放已建立的连接,效率低;
UDP 协议:
- 将数据、源、目的封装成数据包,不需要建立连接;
- 每个数据报的大小限制在 64K 内;
- 因无需连接,所以不可靠;
- 发送数据结束时,无需释放资源,速度快
4.netstat 指令
- netstat -an : 可以查看当前主机网络情况,包括端口监听情况和网络连接情况
- netstat -an | more : 可以分页显示
- 需要在 dos 控制台下 执行
- Listenning 表示某个端口在监听
- 细节: 客户端 和 服务端建立 socket 连接后,客户端也是有一个随机的端口
二、InetAddress 对象
通过 InetAddress 对象,可以获取 主机名、域名、IP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
public class API_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
InetAddress localHost = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println(localHost);
InetAddress name = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
System.out.println(name);
InetAddress name1 = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
System.out.println("根据域名获取 = "+name1);
String add = name1.getHostAddress();
System.out.println("name1 的知己地址 = "+add);
String hostName = name1.getHostName();
System.out.println("name1 的域名 = "+hostName);
}
}
localhost/127.0.0.1
localhost/127.0.0.1
www.baidu.com/112.80.248.75
112.80.248.75
www.baidu.com
|
三、Socket(套接字)
socket 介绍:
- 通信的两端都要有 Socket,是两台机器间通信的端点;
- 网络通信其实就是 Socket 间的通信;
- Socket 允许程序把网络连接当成一个流,数据在两个 socket 间通过 IO 传输;
- 一般主动发起通信的应用程序属于客户端,等待通信请求的为服务端;
- 服务器监听端口:
- ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
- 服务器连接阻塞:
- Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
- 客户端连接服务器:
- Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999);
- 输入流、输出流 结束标识符:
- socket.shutdownInput();
- socket.shutdownOutput();
- 字符流通信时需要手动刷新
1. 字节流 socket 通信
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public class SocketClient1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999);
System.out.println("客户端 socket= "+socket);
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("hello,server".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
socket.shutdownOutput();
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int data = 0;
while ((data = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, data));
}
socket.shutdownInput();
outputStream.close();
inputStream.close();
socket.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
public class SocketServer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("服务器 socket= "+socket);
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int data = 0;
while ((data = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,data));
}
socket.shutdownInput();
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("hello,client".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
socket.shutdownOutput();
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
|
2. 字符流 socket 通信
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public class SocketClient2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999);
System.out.println("服务器已连接");
OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream();
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(out));
bw.write("hello,server");
bw.flush();
socket.shutdownOutput();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String data;
while ((data = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(data);
}
socket.shutdownInput();
br.close();
bw.close();
socket.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public class SocketServer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(9999);
System.out.println("服务器启动~");
Socket socket = server.accept();
System.out.println("客户端已连接");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String data;
while ((data = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(data);
}
socket.shutdownInput();
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
bw.write("hello,client");
bw.flush();
socket.shutdownOutput();
br.close();
bw.close();
socket.close();
server.close();
}
}
|
3.socket 文件传输
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public class Client1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 8888);
String filePath = new File("").getAbsolutePath() + "/src/com/socket_/通友全球聊-电子版权证书.png";
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(filePath);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int data;
while ((data = fis.read(bytes))!= -1){
os.write(bytes, 0, data);
}
socket.shutdownOutput();
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String da;
while ((da = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.print(da);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public class Server1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888);
Socket socket = server.accept();
String filePath = new File("").getAbsolutePath() + "/src/1.png";
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int data;
while ((data = is.read(bytes)) != -1){
fos.write(bytes,0,data);
}
socket.shutdownInput();
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("收到图片".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
is.close();
os.close();
socket.close();
server.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
public class StreamUtils {
public static byte[] streamToByteArray(InputStream is) throws Exception{
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte []b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(b))!= -1){
bos.write(b,0,len);
}
byte[] array = bos.toByteArray();
bos.close();
return array;
}
public static String streamToString(InputStream is) throws Exception{
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine())!=null){
buffer.append(line + "\r\n");
}
return buffer.toString();
}
}
|
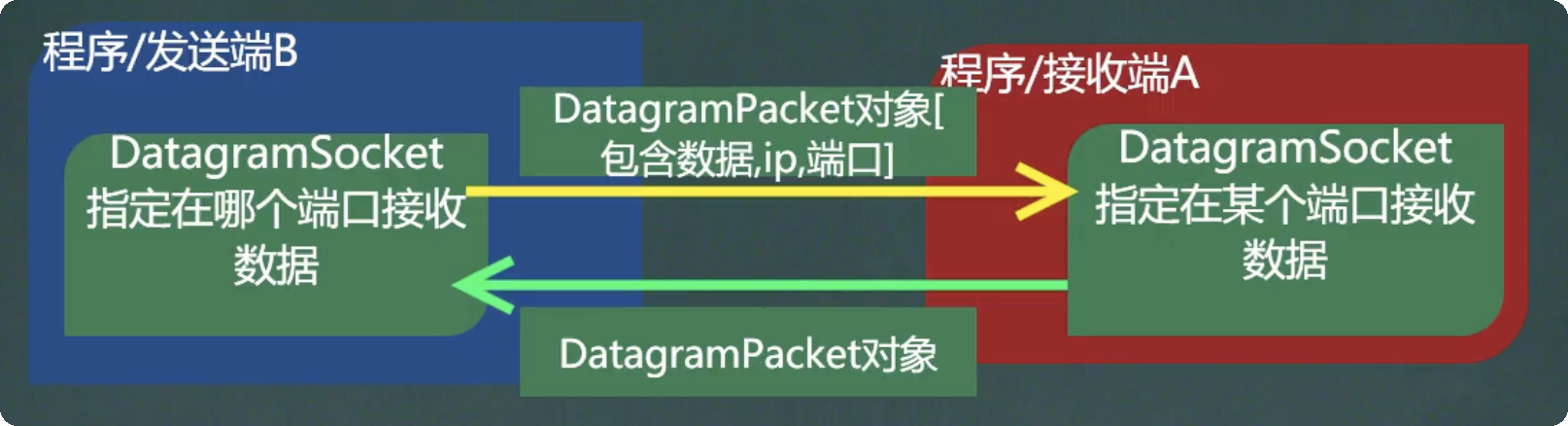
四、UDP 协议
UDP 说明:
- 发送和接收数据都是通过 DatagramSocket 对象 完成;
- 没有明确的服务端 和 客户端 之分,演变成数据的发送端和接收端;
- 发送 和 接收 数据时,需要对 DatagramPacket 对象 进行拆装包;
- UDP 协议的数据包最大为 64K;
- DatagramSocket 可以指定在某个端口接收数据;

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public class UDPReceiver1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket socket= new DatagramSocket(9999);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length);
socket.receive(packet);
int length = packet.getLength();
byte[] data = packet.getData();
String s = new String(data, 0, length);
System.out.println(s);
byte[] bytes1 = "ok,莫得问题".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
DatagramPacket packet1 = new DatagramPacket(bytes1, bytes1.length, InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 8888);
socket.send(packet1);
socket.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public class UDPReceiver2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket socket= new DatagramSocket(8888);
byte[] bytes = "hello, 晚上一起吃火锅啊".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getLocalHost(),9999);
socket.send(packet);
byte[] bytes1 = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet1 = new DatagramPacket(bytes1, bytes1.length);
socket.receive(packet1);
int length = packet1.getLength();
byte[] data = packet1.getData();
System.out.println(new String(data, 0,length));
socket.close();
}
}
|