一、枚举
枚举属于一种特殊的类,里面只包含一组有限的特定的对象。
1.自定义枚举
- 不需要提供 setxxx 方法,防止属性被修改;
- 对枚举对象或属性使用 final 和 static 共同修饰,实现底层优化
- (public final static 返回值类型 对象名);
- 枚举对象名通常全部大写;
- 枚举对象根据需要,可以有多个属性
- 构造器私有化;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
public class Enumeration01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Season.AUTUMN);
}
}
class Season{
private String name;
private String desc;
public final static Season SPRING = new Season("春天", "温暖");
public final static Season SUMMER = new Season("夏天", "炎热");
public final static Season AUTUMN = new Season("秋天", "凉爽");
public final static Season WINTER = new Season("冬天", "寒冷");
private Season(String name, String desc) {
this.name = name;
this.desc = desc;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
}
|
2.使用关键字 enum
- 使用 enum 关键字定义枚举类时,不用写 class
- 枚举定义的常量需要放在 枚举类的首行
- 定义多个常量时,需要用“,”逗号隔开,结尾用 “;”
- 使用无参构造器定义枚举常量时,可以不用写 小括号;
- enum 定义的枚举类 实际上 继承了 Enum 类
- enum 实现的枚举不能继承类(已经隐式继承了 Enum 类),但是可以继承接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| public class Enumeration02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Season2.AUTUMN);
}
}
enum Season2{
SPRING("春天", "温暖"),SUMMER("夏天", "炎热"),AUTUMN("秋天", "凉爽"),WINTER("冬天", "寒冷");
private String name;
private String desc;
private Season2(String name, String desc) {
this.name = name;
this.desc = desc;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Season{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", desc='" + desc + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
|
3. enum 常用方法
| toString | Enum 类已经重写了该方法,返回的是当前对象名 |
|---|
| toString | 子类可以重写该方法,用于返回对象的属性信息 |
| name | 返回当前对象名(常量名),子类不能重写 |
| ordinal | 返回当前对象的位置号,默认从 0 开始 |
| values | 返回当前枚举类中所有的常量 |
| valuesOf | 将字符串转成枚举对象,要求字符串必须位已有的常量名,否则报异常 |
| compareTo | 比较两个枚举常量,比较的就是位置号 |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
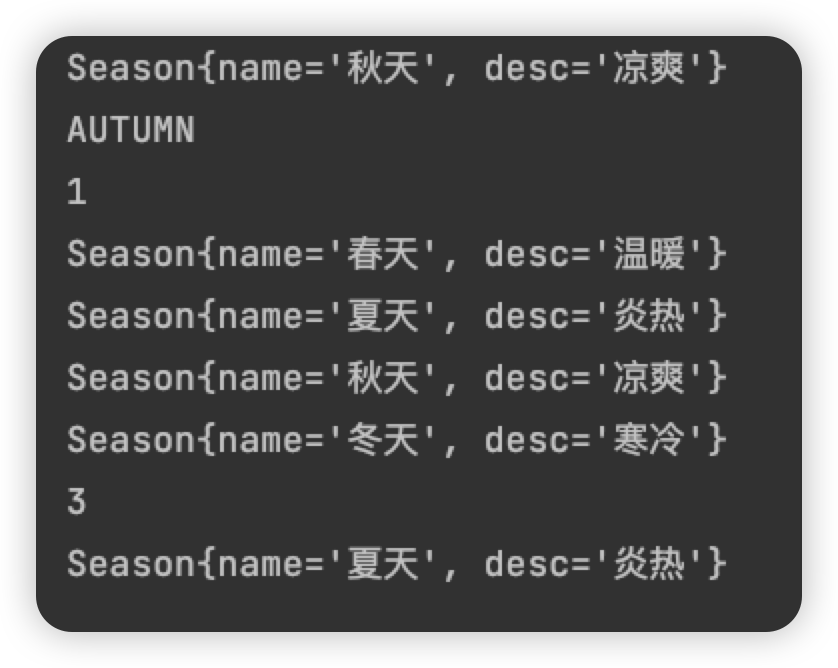
public class Enumeration03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Season2.AUTUMN);
System.out.println(Season2.AUTUMN.name());
System.out.println(Season2.SUMMER.ordinal());
Season2[] s = Season2.values();
for (Season2 season:s) {
System.out.println(season);
}
System.out.println(Season2.WINTER.compareTo(Season2.SPRING));
Season2 summer = Season2.valueOf("SUMMER");
System.out.println(summer);
}
}
enum Season3{
SPRING("春天", "温暖"),SUMMER("夏天", "炎热"),AUTUMN("秋天", "凉爽"),WINTER("冬天", "寒冷");
private String name;
private String desc;
private Season3(String name, String desc) {
this.name = name;
this.desc = desc;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Season{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", desc='" + desc + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
|

二、注解(Annotation)
- 注解 也被称为元数据,用于修饰解释 包、类、方法、属性、构造器、局部变量等数据信息;
- 注解 不会影响程序逻辑,但是注解可以被编译运行,相当于嵌入在代码中的补充信息;
- 在 JavaSE 中用于标记过时的功能、忽略、警告等,在 JavaEE 中用来配置应用程序的任何切面;
三种基本的 Annotation:
- @Override : 限定某个方法,是重写父类方法,该注解 只能用于方法;
- @Deprecated : 用于表示程序元素(类、方法等)已过时;
- @SuppressWarnings : 抑制编译器警告;
@interface :不是接口,其表示该类是一个注解类
@Target : 是修饰注解的注解,也叫元注解
@Retention : 指定注解的作用范围
@Inherited : 表示子类会继承父类的注解
如:
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface Override {}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
public class Annotation01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Son son = new Son();
son.fly();
son.eat();
}
}
class Father{
public void fly(){
System.out.println("Father fly~~~");
}
}
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
class Son extends Father{
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("Son fly~~~");
}
@Deprecated
public void eat(){
System.out.println("Son est...");
}
}
|
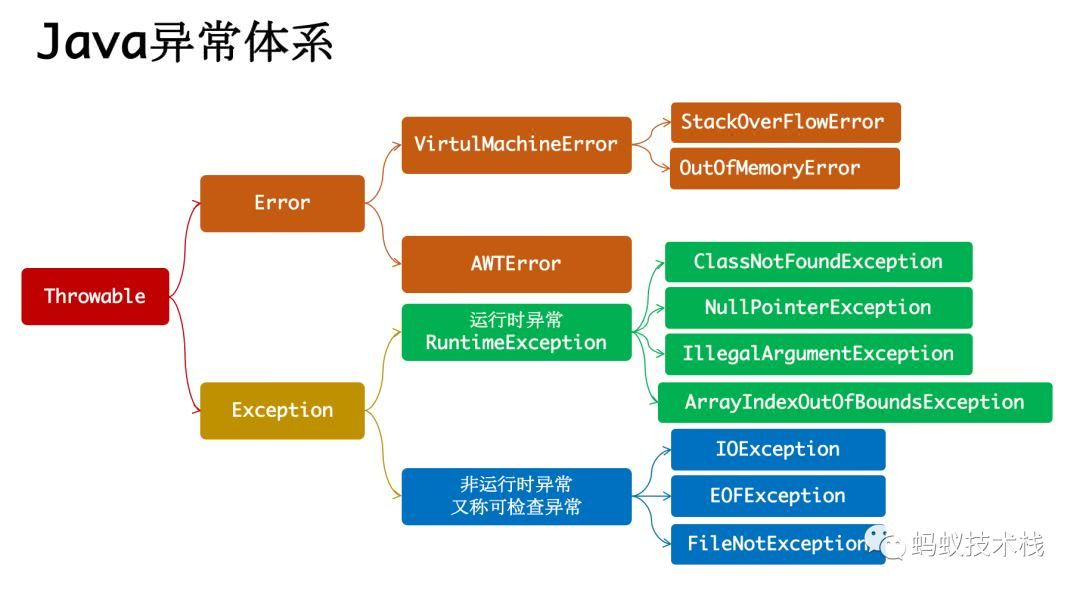
三、异常(Exception)
将程序执行中发生的不正常情况称为 异常
异常事件可分为两类:
- Error : 虚拟机无法解决的严重问题
- 如: 资源耗尽、JVM 系统内部错误等
- Exception : 其他因编程错误或偶然的外在因素导致的一般性问题,可以用针对性代码进行处理;
- 如: 空指针访问,网络中断等;
- Exception 分为两类:
- 运行时异常 : 编程时的逻辑错误
- 编译时异常 : 编译器要求必须处理的异常

异常处理方式:
- try-catch-finally
- 快捷键: option + command + t
- 程序员在代码中捕获发生的异常,自行处理
- throws
- 将发生的异常抛出,交给调用者来处理,最顶级的处理者是 JVM;
try-catch-finally:
- try{} : 放置可能出现异常的代码;
- cath{} : 捕获异常,在 cath 中处理
- 如果没有发生异常,则不执行 cath 中的代码;
- 可以创建多个 cath 来捕获不同的异常;
- 多个异常捕获时,子类异常写在前面,父类异常写在后面;
- finally{} : 不管是否发生异常,finally 都要执行;
- 通常将释放资源的代码放在 finally 中。
- 如果没有 finally,程序是可以通过的
1. try - catch - finally
常见的运行时异常:
| NullPointerException | 空指针异常 | 程序在需要对象的地方使用了 null,则抛异常 |
|---|
| ArithmeticException | 数学运算异常 | 异常运算条件时,抛异常 |
| ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException | 数组下标越界异常 | 下标大于数组下标,抛异常 |
| ClassCastException | 类型转换异常 | 将对象强转为不是其子类时,抛异常 |
| NumberFormatExption | 数字格式不正确异常 | 字符串转为数字时,字符串不能转数字,抛异常 |
try - catch - finally 执行顺序:
- 如果没有出现异常,则执行 try 块中的所有语句,不执行 catch 块中的语句
- 如果有 finally,最后还序号执行 finally 里面的语句;
- 如果出现异常,则 try 块中异常发生后,try 块剩下的语句不再执行;
- 将执行 catch 块中的语句,如果有 finally,最后还需要执行 finally 里面的语句。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| public class Exception01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String str = "hello";
int a = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("字符串转为数字:" + a);
Person person = new Person();
person = null;
System.out.println(person.getClass());
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("程序异常:" + e.getMessage());
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常" + e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("捕获所有的异常" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("不管程序是否异常,都会执行");
}
System.out.println("程序继续执行~");
}
}
class Person {
}
|
2.throws
常见的编译异常:
| SQLException | 操作数据库时,查询表可能发生异常 |
|---|
| IOException | 操作文件时,发生的异常 |
| FileNotFoundException | 当操作一个不存在的文件时,发生异常 |
| ClassNotFoundException | 加载类,而该类不存在时,发生异常 |
| EOFException | 操作文件,到文件末尾,发生异常 |
| IIIegalArguemenException | 参数异常 |
throws:
- 将异常抛出,交给调用者来处理
- 如果程序没有显式的异常处理,则默认为 throws
注意事项:
- 编译异常,程序必须处理;
- 运行异常,程序如果没有处理,则默认是 throws 的方式处理;
- 子类重写父类的方法时,对抛出异常的规定:
- 子类重写的方法,所抛出的异常类型要和父类抛出的异常一致,或者是父类抛出异常的子类
- 在 throws 过程中,如果有 try-catch ,就相当于处理异常,就不必 throws;
thorw 和 thorws 的区别
|
| 意义 | 位置 | 后面跟的东西 |
| —- | —- | —- | —- |
| throws | 异常处理的一种方式 | 方法申明处 | 异常类型 |
| throw | 手动生成异常对象的关键字 | 方法体中 | 异常对象 |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class Exception03 {
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
f1();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("异常处理 ");
}
}
public static void f1() throws FileNotFoundException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d://aa.test");
}
}
|
3.自定义异常
自定义异常 需要继承 Exception 或 RuntimeException
- 如果继承 Exception ,则属于编译异常
- 如果继承 RuntimeException, 则属于运行异常
- 一般情况下,我们把 自定义异常做成 运行时异常,即 继承 RuntimeException 类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Custom01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 810;
if(!(age >=18 && age<= 120)){
throw new AgeException("年龄错误");
}
}
}
class AgeException extends RuntimeException{
public AgeException(String message){
super(message);
}
}
|