一、类
1. 属性
类的属性一般是基本数据类型,也可以是引用数据类型
- 属性的定义语法和变量的定语语法相同;
- 属性如果不赋值,则默认值与数组一致;
1
2
3
4
| class Cat{
String name;
int age;
}
|
2. 创建对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| class Cat{
String name;
int age;
}
Cat cat;
cat = new Cat();
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| class Cat{
String name;
int age;
}
Cat cat = new Cat();
|
二、方法
1.成员方法
1
2
3
| 访问修饰符 返回数据类型 方法名(形参列表){
方法体;
}
|
- 访问修饰符: 控制方法的使用范围,不写则默认
- 四种: public(公共的)、protected(受保护的)、default(默认)、private(私有的)
- 返回数据类型 : 可以返回任意类型;
- 如果有多个返回值时,可以封装成数组返回;
- void:表示没有返回值
- 方法名 : 遵守驼峰命名法的规则,首个单词的首字母小写,其他单词的首字母大写;
- 形参列表: 参数的数量和类型不限制,参数调用时,参数类型必须相同或兼容
- 方法体: 要执行的代码,方法不能嵌套使用;
法的调用:
- 同一个类中的方法可以直接调用
- 不同类之间调用方法时,需要用过类名调用;
- 不同类之间方法的调用和 方法的修饰符相关;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| public class demo01{
public static void main(String[] args){
Person p = new Person();
p.speak();
p.cal01();
p.cal02(100);
p.getSum(3,4);
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public void speak(){
System.out.println("我是一个好人");
}
public void cal01(){
int sum = 0;
for (int i=0; i<=1000; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("1~1000 之和为:"+sum);
}
public void cal02(int n){
int sum = 0;
for (int i=0; i<=n; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("1~"+n+" 之和为:"+sum);
}
public int getSum(int n,int m){
int res = n + m;
return res;
}
}
|
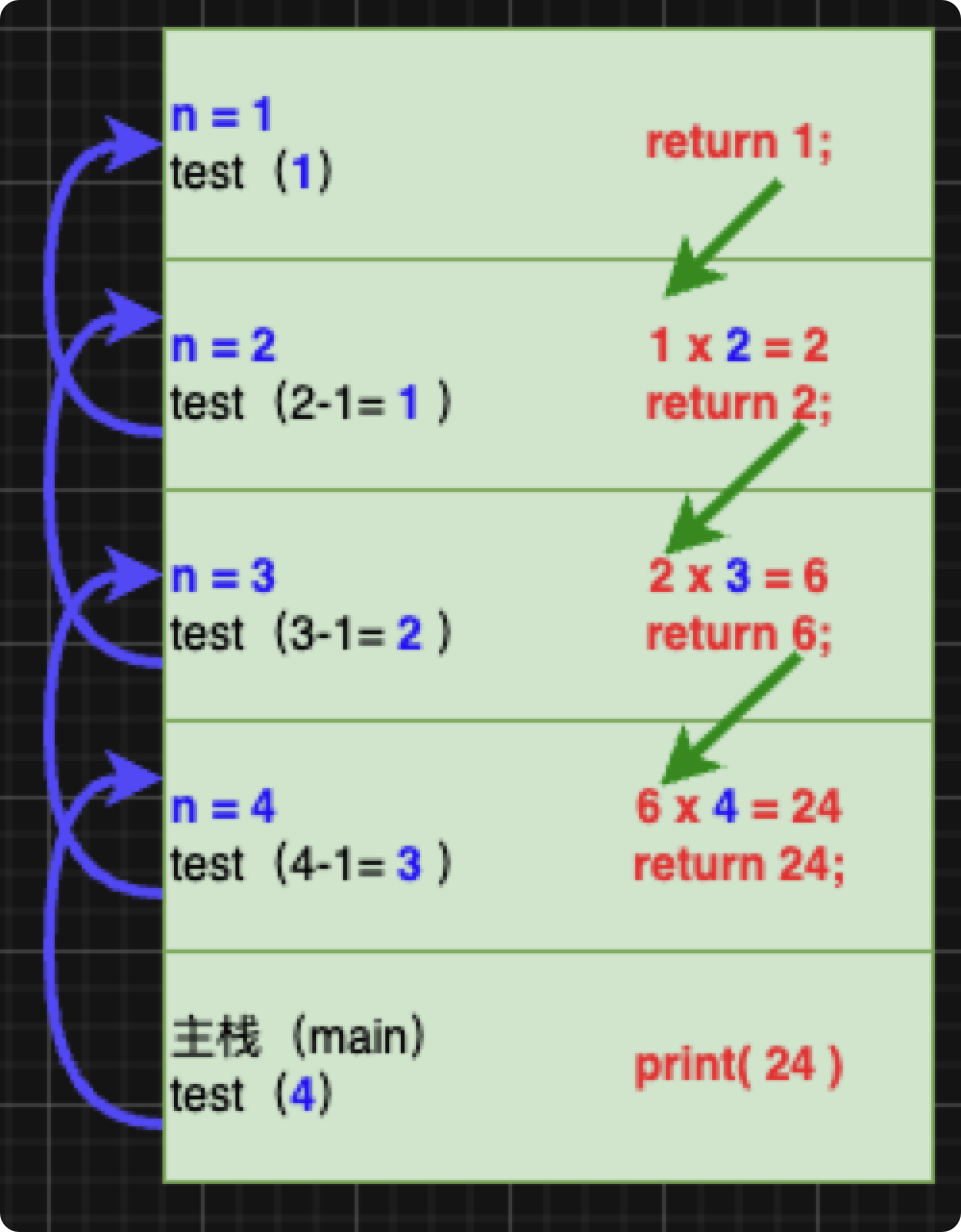
2.递归方法
注意:
- 如果递归方法中使用的是引用类型(比如数组、对象),就会共享该引用类型的数据;
- 递归必须向退出递归的条件逼近,否则就是无限递归
- 递归 就是谁调用,就将结果返回给谁
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class demo01{
public static void main(String[] args){
T t = new T();
int a = t.test(4);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
class T{
public int test(int n){
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}else{
return test(n-1)*n;
}
}
}
|

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class demo01{
public static void main(String[] args){
T t = new T();
int a = t.test(7);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
class T{
public int test(int n){
if (n < 3) {
return 1;
}else{
return test(n-1) + test(n-2);
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class demo01{
public static void main(String[] args){
T t = new T();
int a = t.test(1);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
class T{
public int test(int day){
if (day == 10) {
return 1;
}else{
return (test(day + 1)+1)*2;
}
}
}
|
3. 方法重载
java 中允许同一个类中,多个方法同名,但是要求形参不一致
注意事项:
- 方法名: 必须相同
- 参数列表: 必须不同
- 返回值: 无要求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| public class demo01{
public static void main(String[] args){
MyCalculator myCalculator = new MyCalculator();
System.out.println(myCalculator.calculate(3,4));
System.out.println(myCalculator.calculate(3.3,4));
System.out.println(myCalculator.calculate(3,4.4));
System.out.println(myCalculator.calculate(3,4,5));
}
}
class MyCalculator{
public int calculate(int n1, int n2){
return n1+n2;
}
public double calculate(int n1, double n2){
return n1 + n2;
}
public double calculate(double n1, double n2){
return n1 + n2;
}
public int calculate(int n1,int n2,int n3){
return n1+n2+n3;
}
}
|
4.可变 形参
java 中允许将同一个类中多个同名同功能但参数个数不用的方法,封装成一个方法
1
| 访问修饰符 返回类型 方法名(数据类型... 参数名)
|
- 可变形参可以当做 数组 使用
- 可变参数的 实参可以是数组
- 可变参数可以和普通类型的参数放在同一形参列表,并且可变参数需要放在最后
- 一个方法中只能有一个可变参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| public class demo01{
public static void main(String[] args){
HspMethod hspMethod = new HspMethod();
System.out.println(hspMethod.mySum());
System.out.println(hspMethod.mySum(4));
System.out.println(hspMethod.mySum(3,4));
System.out.println(hspMethod.mySum(3,4,5));
}
}
class HspMethod{
public int mySum(int... nums){
if (nums.length > 1) {
int temp = 0;
for (int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) {
temp += nums[i];
}
return temp;
} else {
System.out.println("参数个数不足");
return -1;
}
}
}
|
三、变量的作用域
全局变量: 属性,作用域为整个类,可以不用赋值,有默认值
局部变量:除了属性之外的其他变量,作用于代码块中,必须赋值,没有默认值
属性和局部变量同名时,遵守就近原则
属性可以被本类使用或者被其他类通过类调佣使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| class Cat{
String name;
int age;
public void cat(){
String color = "黑色";
}
}
|
四、构造器
构造器: 类的一种特殊方法,主要作用是对已经完成的新对象的初始化
1
2
3
| [修饰符] 方法名(形参列表){
方法体;
}
|
- 构造器的修饰符可以默认,也可以是其他的
- 构造器没有返回值
- 方法名与类名相同
- 在创建对象时,系统会自动调用该类的构造器完成对象的初始化
- 构造器也可以进行重载
- 如果没有定义构造器,系统会默认生成一个构造器
- 如果定义了构造器,默认的构造器会被覆盖,如果要调用默认的构造器,需要显示的重新定义一个
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] arge){
Person p1 = new Person("张三", 20);
}
}
public class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person(String pName, int pAge){
name = pName;
age = pAge;
}
}
|
五、this 关键字
this : 表示当前调用的对象
- this 关键字 可以用来访问本类的 属性、方法、构造器
- 访问成员方法: this.方法名(参数列表)
- 访问构造器:this(参数列表);
- 如果要访问构造器,语句必须放在第一条
- 只能在构造器中使用(在构造器中访问另一个构造器)
- this 用于区分当前类的属性和局部变量
- this 不能在类定义的外部使用,只能在类定义的方法中使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public class demo01{
public static void main(String[] args){
Person p1 = new Person("张三", 15);
Person p2 = new Person("李四", 20);
System.out.println(p1.test(p2));
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public boolean test(Person P){
return this.name.equals(P.name) && this.age == P.age;
}
}
|